A smart contract is a program that lives on the blockchain. When you interact with a smart contract, you ask it to read data or perform an action. Some contract interactions only read information, like checking a balance. Others change state, like sending tokens or updating permissions.
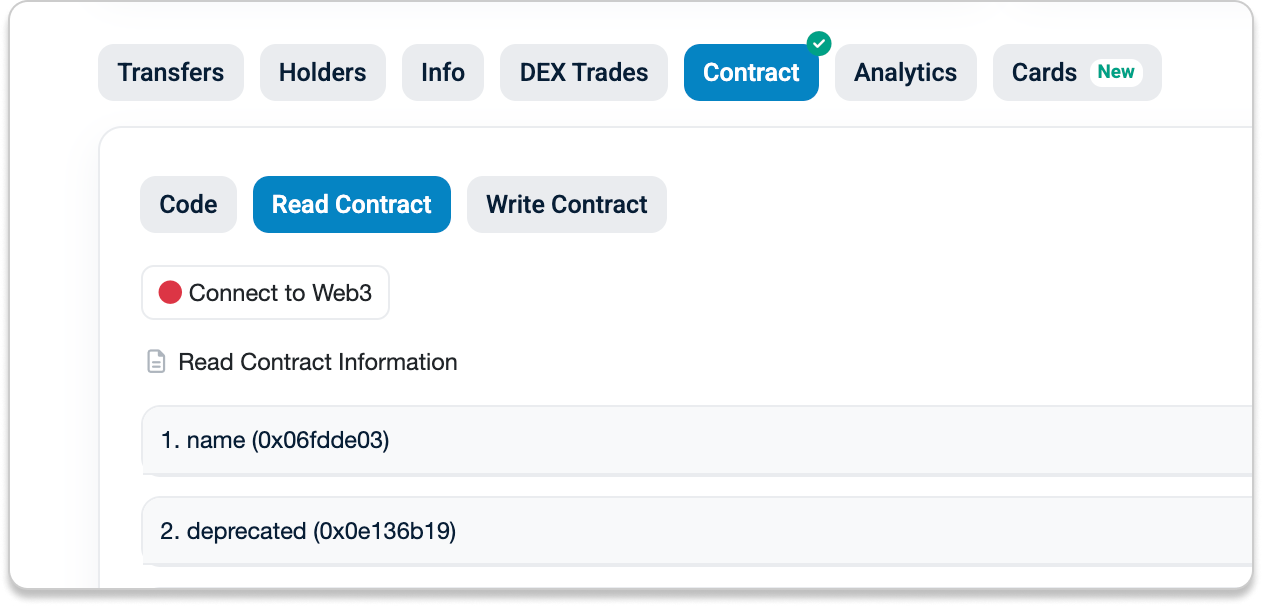
On Etherscan, you can interact with smart contracts using the Read Contract and Write Contract tabs on a contract page. These let you inspect and interact with a contract directly, even when no separate user interface is available.
- Read Contract lets you fetch and view public data that the contract exposes. These calls do not change the blockchain and do not cost gas.
- Write Contract lets you submit transactions that change state, such as transferring tokens or approving allowances. These require signing with a wallet and cost gas.
Note: When you interact with smart contracts on Etherscan using the Read or Write tabs, the request runs in your browser and is sent directly to an Ethereum node to fetch onchain data. It does not pass through Etherscan’s website servers. For Read Contract queries, the request is sent by default to an Ethereum node operated by Etherscan, but you can connect your own wallet or local node if you want greater privacy and control.
While read-only queries are safe and do not modify the blockchain, write interactions are different. Any transaction you sign can move funds, grant permissions, or permanently change contract state. Once submitted, these actions are usually irreversible.
Before you click “Confirm” in your wallet, use the checklist below to protect your digital assets. The sections that follow cover common risks when interacting with smart contracts and practical steps to reduce them.
- The "Verified" Checkmark
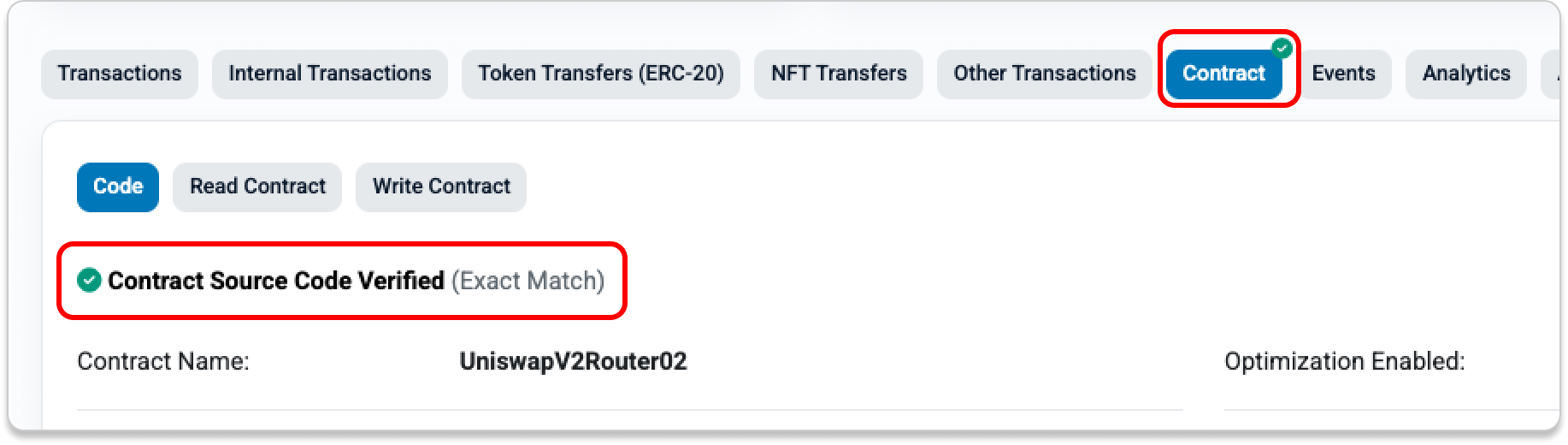
Verified smart contracts on Etherscan display a green checkmark ✅ on the Contract tab. This means the source code is public and matches the bytecode deployed onchain.
“Verified” does not mean the contract is safe to interact with or that it has been audited. It only confirms that the published source code corresponds to what is running on the blockchain.
You can use your preferred LLM or Etherscan’s Code Reader to review the source code and identify potential risks. You can also ask it to explain the specific function and parameters you are about to interact with.
If a contract’s source code is not verified, you cannot see what the contract will do when you sign a transaction. This can include unknowingly granting approvals or permissions that allow malicious actors to spend your funds. Avoid signing transactions you do not fully understand.
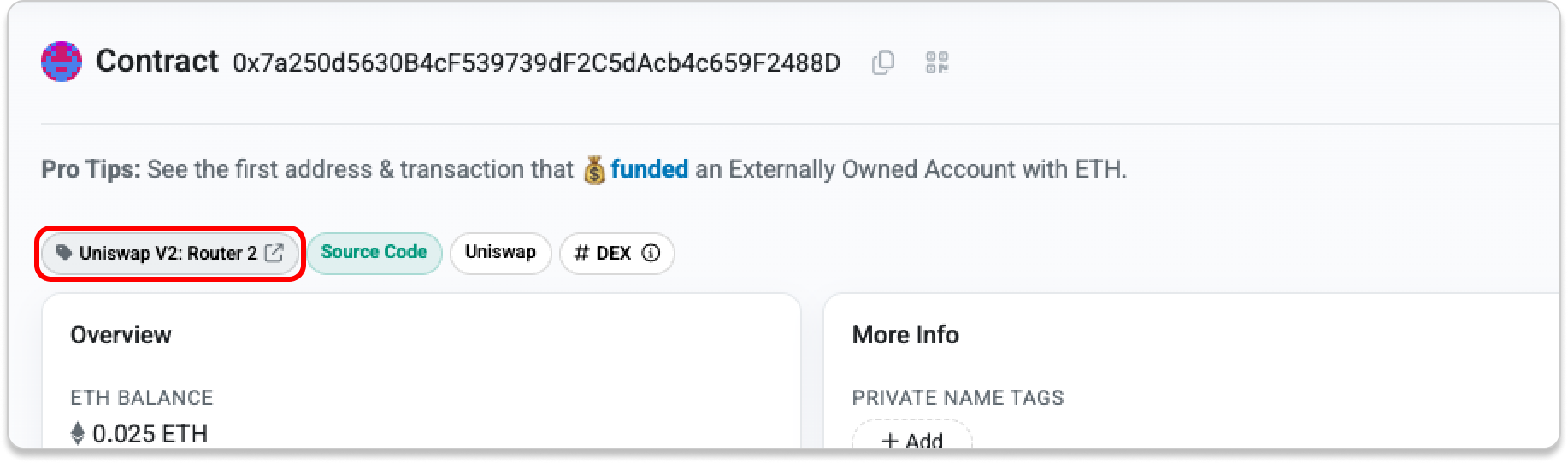
- Public Name Tag
If a contract has a public name tag, you can click it to visit the associated website and find more information about the project.
If no name tag is present, verify the contract address using official project sources before interacting with it.
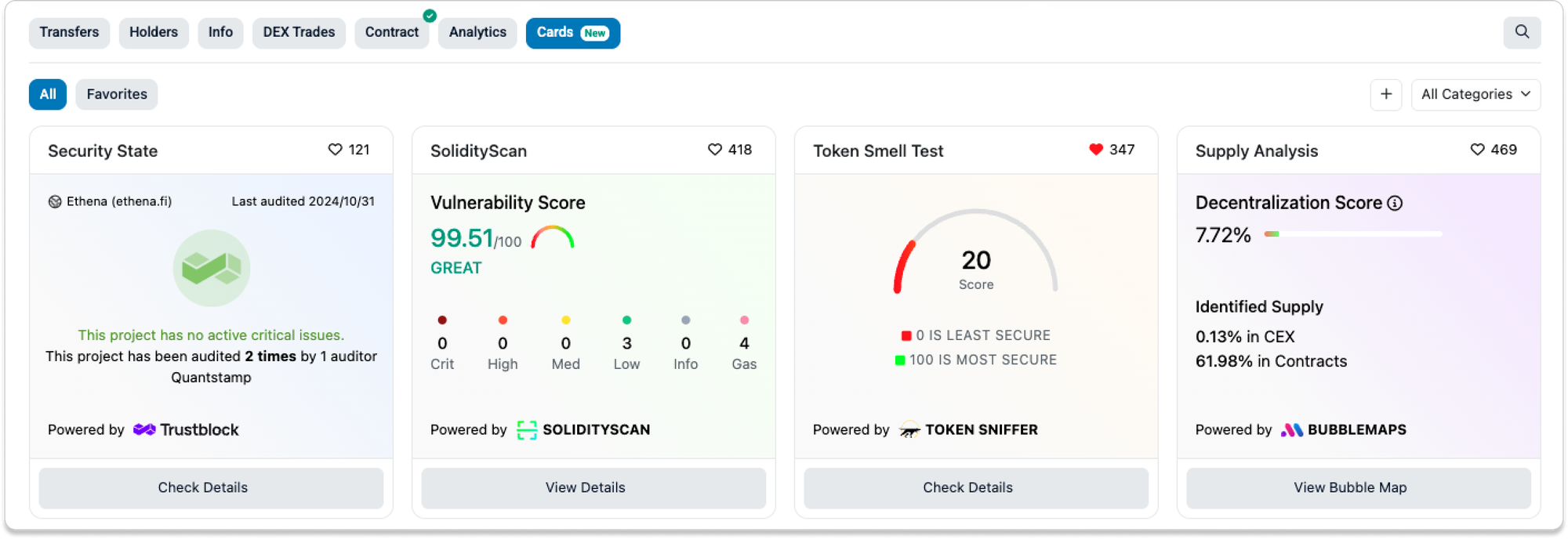
- Additional Insights from Cards
Cards allow credible third parties in the Ethereum ecosystem to surface useful context directly on the explorer. They provide quick signals when you are unsure whether a contract is safe.
For example, the GoPlus Card may flag unverified source code, fake tokens, or buy taxes. Token Sniffer may identify a contract as a scam.
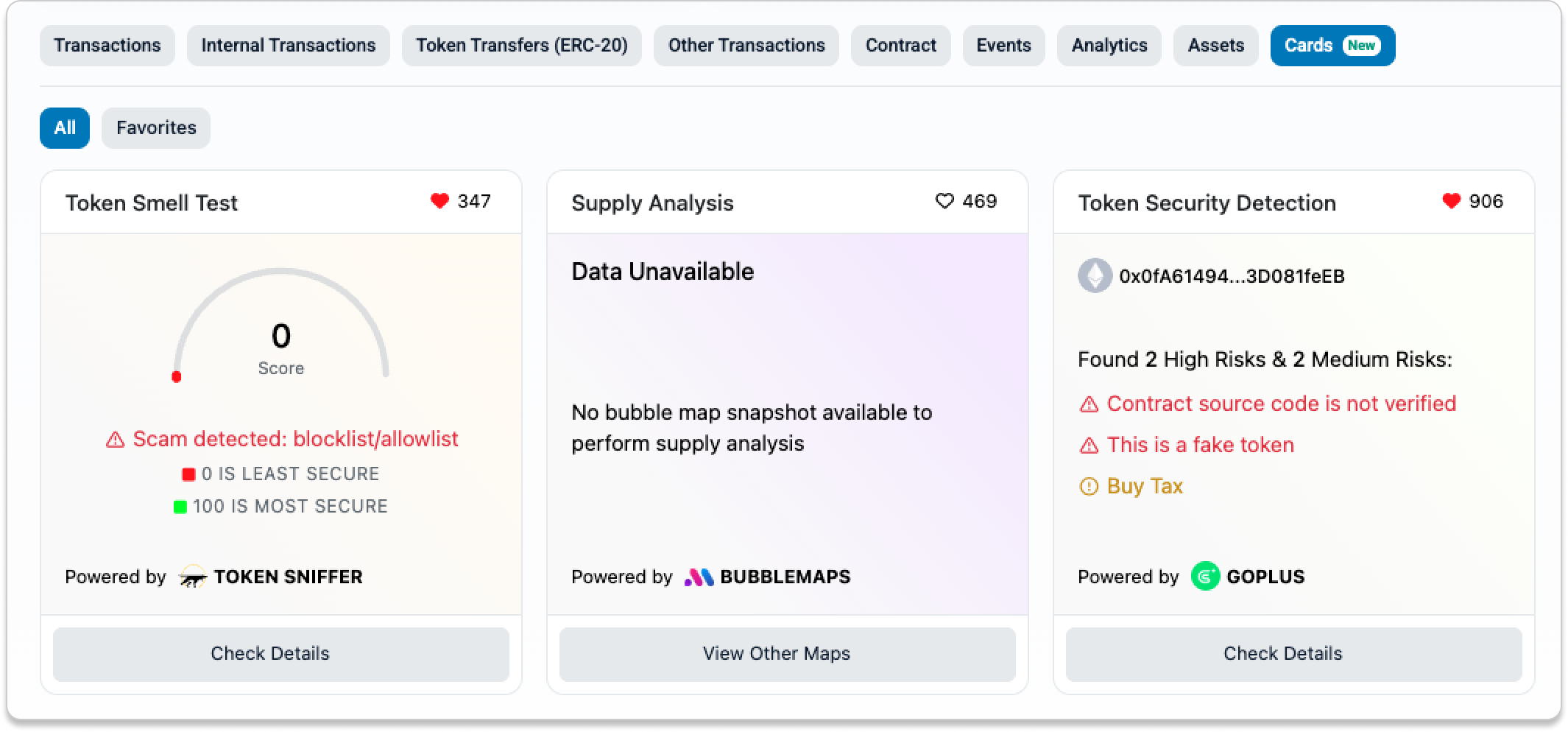
You may also see audit information from Trustblock or a vulnerability score from SolidityScan.
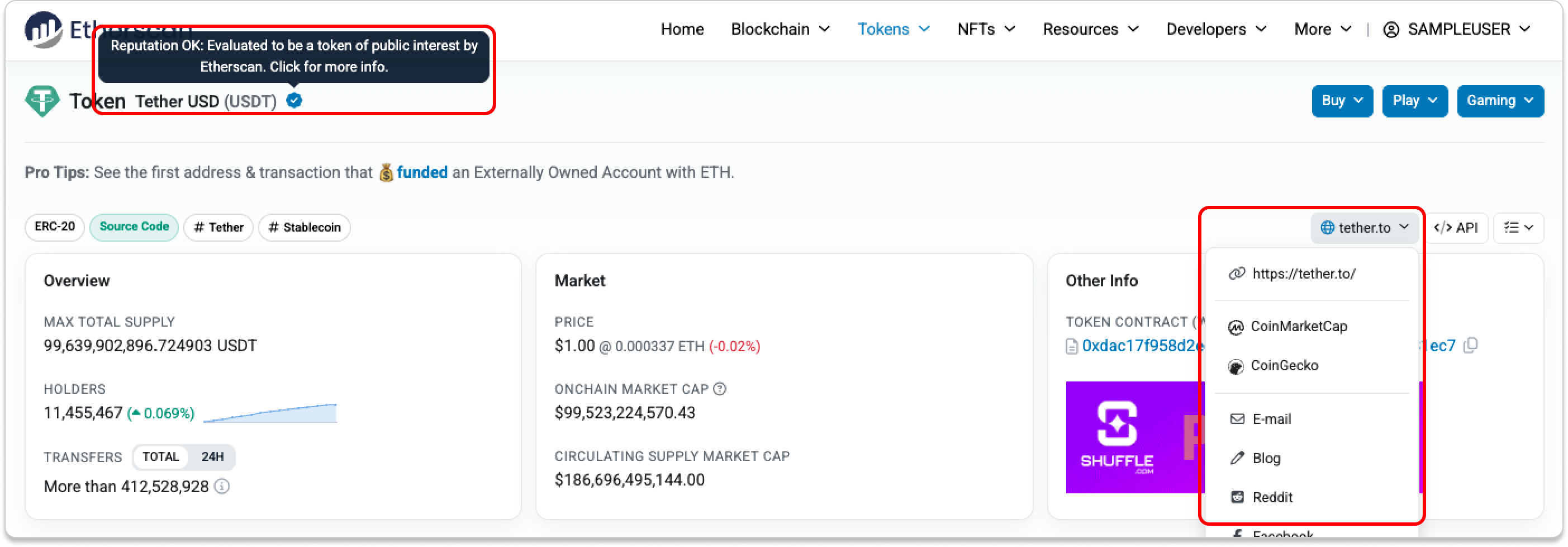
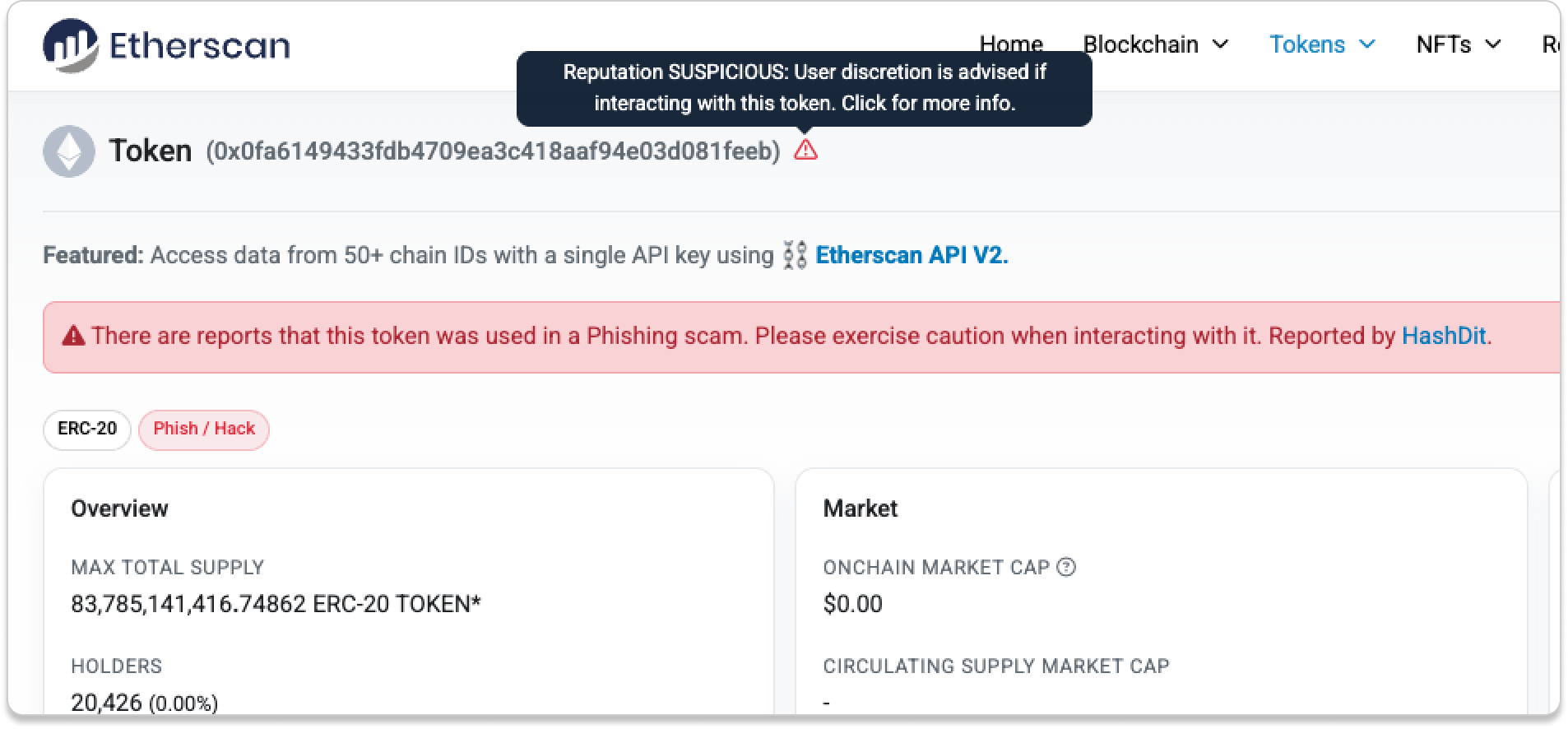
- Token Reputation
Not all tokens are created equal. When interacting with a token contract, check its token reputation to get a general sense of risk. Token reputation on Etherscan ranges from OK and Neutral to Unknown, Suspicious, Unsafe, and Spam.
If the token is Suspicious, Unsafe, or Spam, please exercise caution when interacting with it.
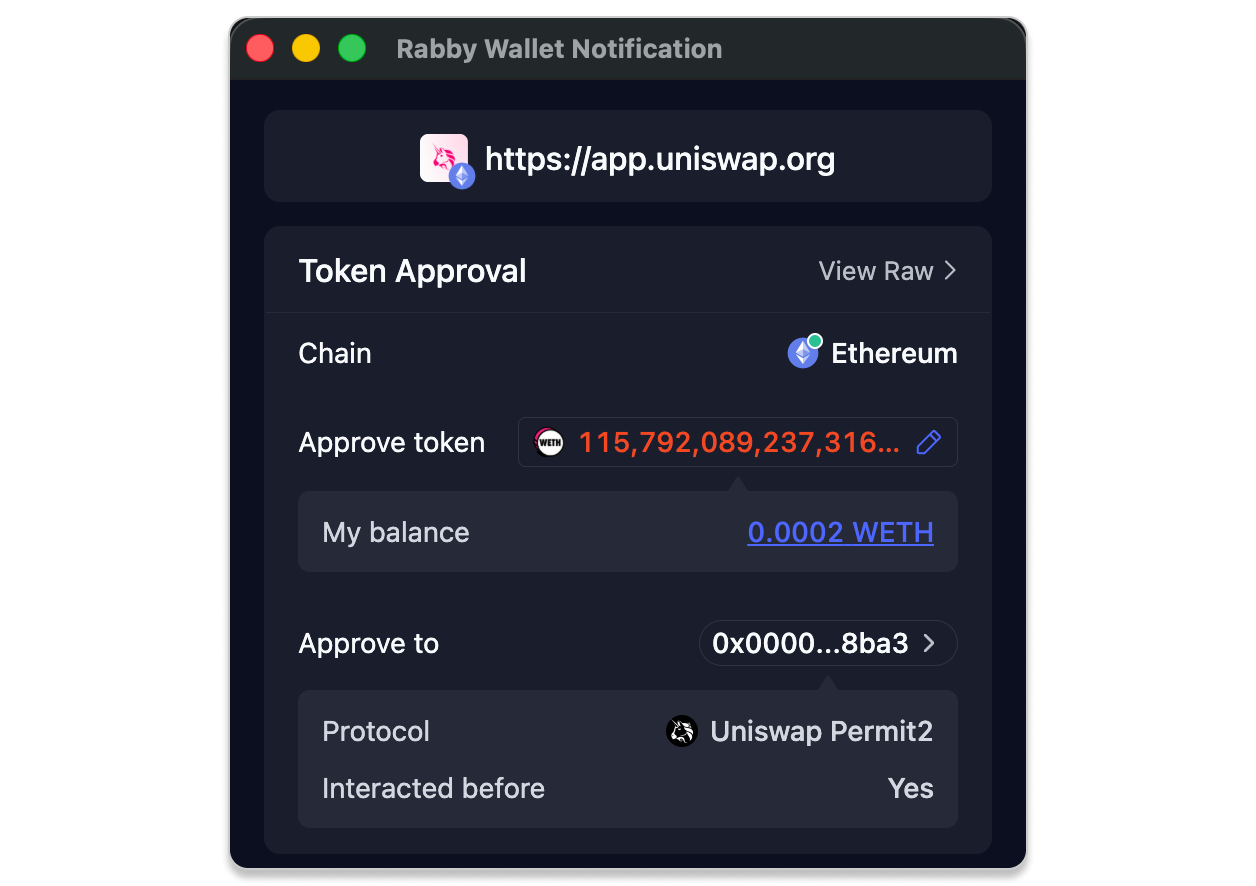
- Limit Token Approvals
When approving tokens for a smart contract, pay attention to the amount you are authorizing. If you approve more than you intend to spend, the contract can later use the remaining allowance without requiring another signature.
Review and revoke unused approvals regularly using the Token Approval tool.
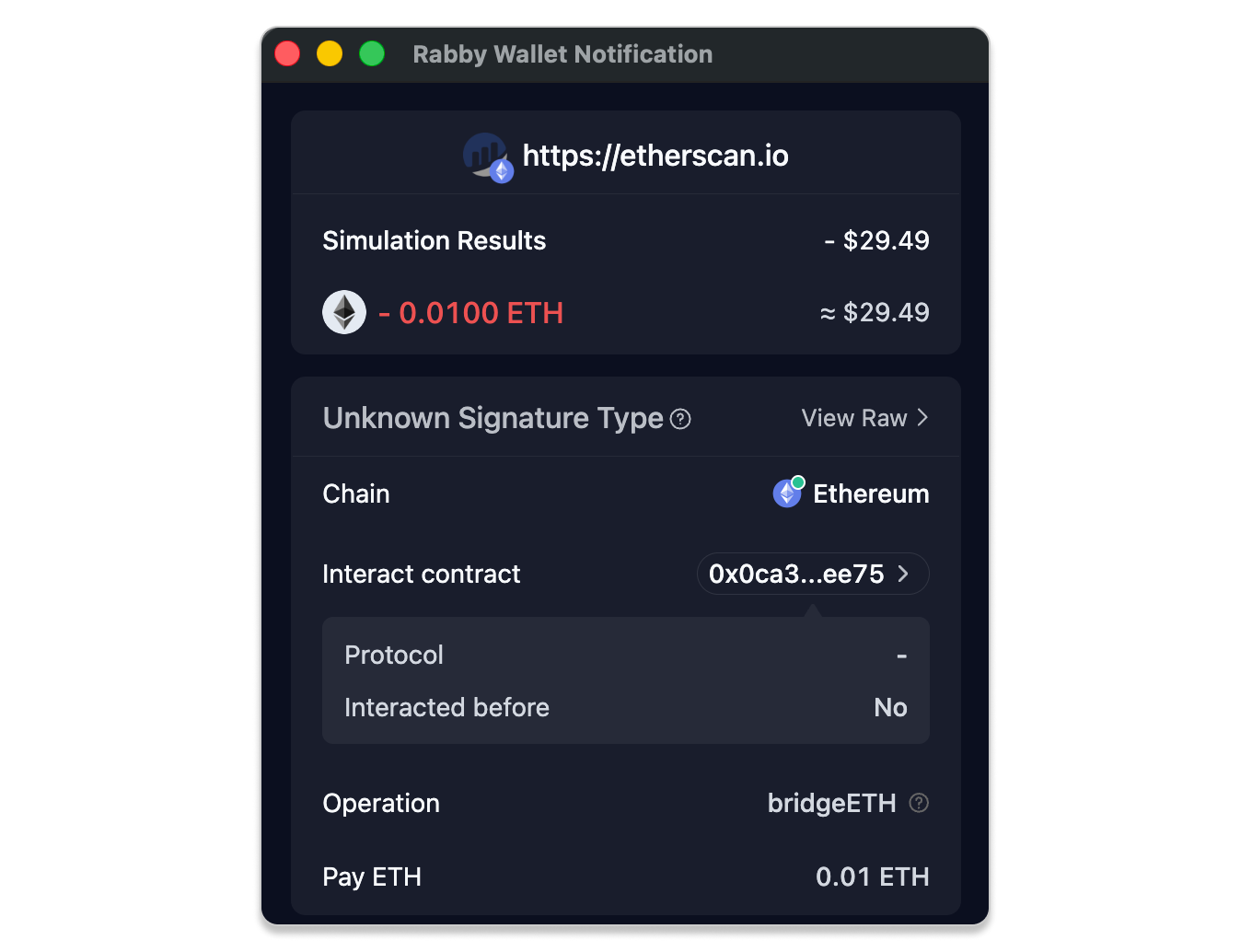
- Read the Transaction Simulation
Modern wallets now show a simulation of what will happen before you sign a transaction.
If the simulation warns that assets may be drained or shows tokens leaving your wallet unexpectedly, reject the transaction. If anything looks different from what you intended, stop and review.
Final Reminder
Etherscan helps you inspect and explore onchain data, but it does not audit or guarantee the safety of contracts. You are responsible for understanding every transaction you sign.
If something feels unclear or rushed, it is usually safer to pause and verify before proceeding.